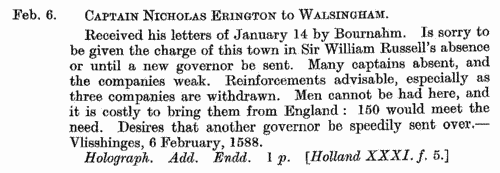Will Surname Ancestry ResultsOur indexes 1000-1999 include entries for the spelling 'will'. In the period you have requested, we have the following 115 records (displaying 1 to 10): Single Surname Subscription | | | Buying all 115 results of this search individually would cost £624.00. But you can have free access to all 115 records for a year, to view, to save and print, for £100. Save £524.00. More... |
These sample scans are from the original record. You will get scans of the full pages or articles where the surname you searched for has been found. Your web browser may prevent the sample windows from opening; in this case please change your browser settings to allow pop-up windows from this site. Inhabitants of London
(1275-1298)
Liber Horn or the Lesser Black Book, now known as Letter Book A of the City of London contains enrolments of recognizances between inhabitants, particularly citizens, for sums of money lent or due; grants of pieces of land or property; and various records relating to the city administration. The letter books are so called because they were lettered from A to Z and from AA to ZZ, not because they were books of letters. Letter Book A was edited by Reginald R. Sharpe for the corporation and printed in 1899.
WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Freemen and citizens of London
(1291-1309)
Letter Book C of the City of London contains enrolments of recognizances between inhabitants, particularly citizens, for sums of money lent or due; grants of pieces of land or property; and various records relating to the city administration, minor infractions, &c. The text was edited by Reginald R. Sharpe and printed by order of the Corporation of the City of London in 1901.WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Taxpayers in Sussex
(1524-1525)
By Act of Parliament of 1523 (14 & 15 Hen. III, c. 16) a general subsidy was raised, spread over four years, from laymen, clergy and peers. In each of the first two years 1s in the £ was raised from annual income from land; 1s in the £ on capital goods worth over £2 and under £20; and a flat payment of 4d on goods worth from £1 to £2, and also by persons aged 16 and upwards in receipt of £1 per annum in wages. In the third year a further shilling in the pound was payable on land worth £50 and upwards a year; and in the fourth year a shilling in the pound on goods worth £50 and upwards. To raise this revenue, returns were required from every hundred, parish or township. In Sussex, the returns for 1524 and 1525 cover the city of Chichester (divided into Estrata, Westrata, Southstrata, North[strata] and Palenta), the borough of Midhurst, and then the rest of the county divided into rapes, within those into hundreds, and within those into boroughs, tithings, liberties, townships or parishes. It is important to note that the cinque ports of Hastings, Rye and Winchelsea were exempt from the subsidy, except for alien inhabitants; and that the town of Westbourne was also exempted 'as the town was lately destroyed by fire'. Aliens are noted as such, sometimes with nationality; and Brighthelmstone (Brighton), which had been burnt by the French in 1514, is only represented fragmentarily. The Sussex Record Society published this transcript and edition by Julian Cornwall of the 1524 and 1525 returns: the 1524 return was used for the main transcript where possible, names peculiar to the 1524 lists being marked with an asterisk, and those with amendments in 1524 with a dagger. At the foot of each 1524 return the new names from 1525 are given. Only the amount of the assessment is printed (m. = marks). Letters prefixed to the sum give the basis of the assessment, no letter (or G) meaning that it was on goods - A, annual wages; D, annual wages of day-labourers; F, fees or salaries of office; L, lands; P, profits; W, wages; x, no basis stated. WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
| Militia in Andersfield hundred, Somerset
(1569)
A muster of the ablemen, gunners, light horsemen, pikemen, archers and billmen available from this hundred, compiled by sir Hugh Paulet, sir Maurice Barkeley, sir Ralph Hopton and John Horner in answer to a royal commission of the 11th year of queen Elizabeth. The returns are arranged by tithing. The hundred consisted of the parishes of Broomfield, Creech St Michael, Durleigh, Enmore, Goathurst and Lyng, south of Bridgwater. (The sample shown is from the return for the borough of Axbridge)WILL. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Scottish litigants, rebels and cautioners
(1578-1585)
The Privy Council of Scotland exercised a superior judicial authority in the kingdom, and consequently received and dealt with a constant stream of petitions, as well as dealing with the internal security of the state. This register of the council from 17 June 1578 to 31 July 1585, in the reign of king James VI, was edited by David Masson, and published under the direction of the Lord Clerk Register of Scotland in 1880. Some of the individuals mentioned are the complainants, those of whom they complained, and the sureties on both sides: at this period, some of the complainants are alleging serious attacks, often of a feuding nature. Many of the bonds entered into by the cautioners are promises to keep the peace towards such enemies. Failure to answer to the council when summoned was a serious contempt, leading to being denounced a rebel, with serious consequences. But 'horning' was also used in the pursuit of debts: there was no imprisonment for debt in Scotland, but a creditor could have an obstinate debtor ordered, in the sovereign's name, to pay what was due, failing which, the debtor could be put to the horn, denounced as a rebel, and imprisoned as a rebel. The main text (to page 762) is from the Acta Secreti Concilii, containing the minutes of the Privy Council, and of occasional Conventions of the Estates. After that are printed some miscellaneous Privy Council documents from the same years. The sources most productive of names, the Acta Cautionis and Registration of Bands, are also the most repetitive in form, and are not transcribed verbatim and literatim: nevertheless, one of the editor's rules was for 'All proper names and names of places occurring in the originals to be preserved in the abstracts without exception, and in the exact original spelling.'
WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Ambassadors, ministers, soldiers and spies
(1589)
The State Papers Foreign of queen Elizabeth consist mainly of letters and reports concerning England's relations with continental Europe, particularly the Netherlands and France. January to July 1589. WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
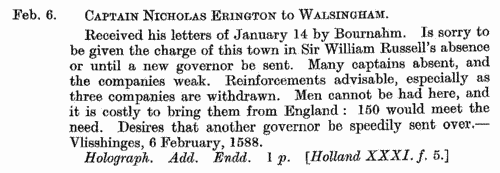
| Scottish litigants, rebels and cautioners
(1585-1592)
The Privy Council of Scotland exercised a superior judicial authority in the kingdom, and consequently received and dealt with a constant stream of petitions, as well as dealing with the internal security of the state. This register of the council from 1 August 1585 to 31 July 1592, in the reign of king James VI, was edited by David Masson, and published under the direction of the Lord Clerk Register of Scotland in 1881. Some of the individuals mentioned are the complainants, those of whom they complained, and the sureties on both sides: at this period, some of the complainants are alleging serious attacks, often of a feuding nature. Many of the bonds entered into by the cautioners are promises to keep the peace towards such enemies. Failure to answer to the council when summoned was a serious contempt, leading to being denounced a rebel, with serious consequences. But 'horning' was also used in the pursuit of debts: there was no imprisonment for debt in Scotland, but a creditor could have an obstinate debtor ordered, in the sovereign's name, to pay what was due, failing which, the debtor could be put to the horn, denounced as a rebel, and imprisoned as a rebel. The main text (to page 774) is from the Acta Secreti Concilii, containing the minutes of the Privy Council, with intermixed Acta Proper (political edicts), Decreta (judicial decisions), Acta Cautionis (acts of caution) and Bands (registration of bonds). After that are printed some miscellaneous Privy Council documents from the same years: additional acts of caution (775-778); ordinances and acts anent the Borders and the North (779-814); and miscellaneous privy council papers (815-834). The sources most productive of names, the Acta Cautionis and Registration of Bands, are also the most repetitive in form, and are not transcribed verbatim and literatim: nevertheless, one of the editor's rules was for 'All proper names and names of places occurring in the originals to be preserved in the abstracts without exception, and in the exact original spelling.'
WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Scottish litigants, rebels and cautioners
(1592-1599)
The Privy Council of Scotland exercised a superior judicial authority in the kingdom, and consequently received and dealt with a constant stream of petitions, as well as dealing with the internal security of the state. This register of the council from August 1592 to May 1599, in the reign of king James VI, was edited by David Masson and published under the direction of the Deputy Clerk Register of Scotland in 1882. The publication brings together the contents of the principal register (Acta Secreti Concilii) with acts and bands (bonds) of caution (surety) from the registers called Acta Cautionis (pp 561-730); Acts and Ordinances relating to the Borders and the North (731-748); and Miscellaneous Privy Council Papers (749-769). Many of the individuals mentioned are the complainants, those of whom they complained, and the sureties on both sides: at this period, many of the complainants are alleging serious attacks, often of a feuding nature. Many of the bonds entered into by the cautioners are promises to keep the peace towards such enemies. Failure to answer to the council when summoned was a serious contempt, leading to being denounced a rebel, with serious consequences.
WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Scottish litigants, rebels and cautioners
(1610-1613)
The Privy Council of Scotland exercised a superior judicial authority in the kingdom, and consequently received and dealt with a constant stream of petitions, as well as dealing with the internal security of the state. This register of the council from July 1610 to February 1613, in the reign of king James VI, was edited by David Masson and published under the direction of the Deputy Clerk Register of Scotland in 1889. The publication starts with the Acta and Decreta, a chronological consolidation of material from Acta Secreti Concilii proper, the Decreta, the Book of Commissions, the Book of Sederunts, the Minute Book of Processes, and The Book of the Isles. There is then a section of Royal and Other Letters (pp. 565-644); then acts and bands (bonds) of caution (surety) from the registers called Acta Cautionis (pp. 647-690); and Miscellaneous Privy Council Papers (693-746). Many of the individuals mentioned are the complainants, those of whom they complained, and the sureties on both sides: at this period, many of the complainants are alleging serious attacks, often of a feuding nature. Many of the bonds entered into by the cautioners are promises to keep the peace towards such enemies. Failure to answer to the council when summoned was a serious contempt, leading to being denounced a rebel, with serious consequences.
WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Merchants and traders in Aberdeen
(1399-1631)
A. M. Munro searched the council registers of the royal burgh of Aberdeen, and compiled this list of burgesses admited to the borough. The entries prior to 1591 were contained in lists engrossed in the council registers at the close of the minutes for the year ending at Michaelmas, but after that date in addition to the annual lists, which are continued, there is almost always a separate minute of admission under the respective dates. The records before 1591 are not only sparser, often with no more than a name, but are also lacking for 1401-1405, 1413-1432, 1434-1435, 1518-1519, 1557 and 1562-1564 - other blanks were filled in from the guildry accounts where such existed. Guild burgesses were allowed unfettered trading rights in Aberdeen; simple burgesses could only deal in Scottish wares (so being barred from the lucrative English and Flemish imports and exports); trade burgesses were limited to their own particular trades; and the council was able ex gratia to create honourary burgesses, who were accorded the full privileges of burgesses of guild and trade, and among whom numbered members of almost every family of note in Aberdeenshire. Burgesses could thus be created by descent, by apprenticeship into a trade, or ex gratia, and in the later portions of this roll the precise circumstances are usually given, sometimes also with the name of a cautioner or surety. Burgesses, masters and cautioners are all indexed here.WILL. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.
|