Gurdon Surname Ancestry ResultsOur indexes 1000-1999 include entries for the spelling 'gurdon'. In the period you have requested, we have the following 124 records (displaying 21 to 30): Single Surname Subscription | | | Buying all 124 results of this search individually would cost £580.00. But you can have free access to all 124 records for a year, to view, to save and print, for £100. Save £480.00. More... |
These sample scans are from the original record. You will get scans of the full pages or articles where the surname you searched for has been found. Your web browser may prevent the sample windows from opening; in this case please change your browser settings to allow pop-up windows from this site. Official Papers
(1651)
The State Papers Domestic cover all manner of business relating to Britain, Ireland and the colonies, conducted by the Council of State, as well as other miscellaneous records. These records are from January to October 1651.
GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Official Papers
(1655-1656)
The State Papers Domestic cover all manner of business relating to Britain, Ireland and the colonies, conducted in the office of the Secretary of State as well as other miscellaneous records. These records are from November 1655 to June 1656: there is also a set of abstracts of navy correspondence.
GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
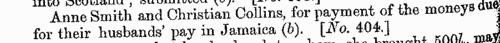
| Official Papers
(1656-1657)
The State Papers Domestic cover all manner of business relating to Britain, Ireland and the colonies, conducted by the Council of State, as well as other miscellaneous records. These records are from July 1656 to May 1657.
GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Colonists and adventurers
(1610-1660)
During this period, the English crown issued charters to companies of adventurers and individual proprietors to establish settlements in Acadia (Nova Scotia), Africa, Amazon, Anguilla, Antigua, Association (Tortuga), Bahamas, Barbadoes, Barbuda, Bermudas (Somers Islands), Canada, Cape Gratia de Dios, Carolina, Bay of Darien, Delaware Bay, Deseada, Dominica, Eleuthera, Enegada, Fernando de Noronho, Floria, Fonseca, Grenada, Guadaloupe, Guiana, Guinea, Henrietta, Jamaica, Long Island, Maine, Marigalante, Maryland, Metalina, Montserrat, Narrangansetts Bay, Nevis, New England (New Plymouth, Massachusetts, Connecticut and New Haven), Newfoundland, New Hampshire, New York, Nova Scotia, Providence Island, Quebec, Redendo, Rhode Island, St Bartholomew, St Brandon, St Christopher's, St Eustache, St Lucia, St Martin, St Vincent, Sembrera, Surinam, Tadousac, Tobago, Todosantes, Trinidad and Virginia. The central archive relating to these ventures up to 1688 amounted to 71 volumes of correspondence, plus 109 entry books containing entries of letters sent to the colonies, of charters, commissions and instructions, minutes and proceedings of the companies and proprietaries that in the first instance governed several of the colonies, journals of the Board of Trade, &c. This archive, called the State Papers, Colonial Series, at the Public Record Office, was calendared for the period through to 1660 by W. Noel Sainsbury, and published in 1860. The first few pages include material as early as 1574, but the bulk of the volume is from 1610 to 1660, and that is indexed here.GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Royalist delinquents in county Durham and Northumberland, their successors, tenants, debtors and creditors
(1648-1660)
King Charles I was executed 30 January 1649, the kingship was abolished and government by a Council of State was established 14 February 1649. Oliver Cromwell became Lord Protector 16 December 1653; died 3 September 1658; and was succeeded by his son Richard, who abdicated 24 May 1659. Charles II was established on the throne 29 May 1660. From 1648 to 1660 parliament sequestrated royalists' estates, restoring many by a process of heavy fines called compounding; this was administered by the Committee for Compounding, working through county committees. These raised considerable amounts of money, money which was vitally necessary for maintaining the parliamentary army's campaigns to subdue opposition in the three kingdoms - England, Scotland and Ireland. The raising and delivery of these monies was the responsibility of the Committee for Advance of Money (C. A. M.). The records of these committees were detailed and extensive, amounting to about 300 volumes, and were calendared for the Public Record Office by Mary Anne Everett Green. Abstracts of the county Durham and Northumberland entries were collated by Richard Welford with a manuscript transcript of the proceedings of the parliamentary commissioners in county Durham surviving in Durham cathedral library, and published by the Surtees Society in 1905. The persons named in these abstracts are not only the delinquents themselves, and those who succeeded them in their estates, but tenants, debtors and creditors, and local constables and officials of the committees.GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Oxford householders
(1665)
Hearth tax was raised by assessing each householder on the number of chimneys to the dwelling. This provided a simple way to make a rough judgment as to the value of the dwelling. In Oxford the returns were made by ward, and then by parish. The return for 1665 (164/154) was edited by J. E. Thorold Rogers and printed for the Oxford Historical Society in 1891. The Roman numerals given are the numbers of hearths: where two or more people are grouped together with one number, it may be assumed that they were heads of separate households sharing a single building with that number of chimneys. Full names are given: only in a few instances is occupation given, nor are the streets indicated; however, there were thirteen ancient parishes in the city, none being very extensive, so a fairly good indication of location is given by the parish name.GURDON. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Suffolk householders
(1674)
Hearth tax was raised by assessing each householder on the number of chimneys to the dwelling. This provided a simple way to make a rough judgment as to the value of the dwelling: paupers were issued exemption certificates, but they too were listed at the end of each return. The returns were made by township, grouped by hundred. A complete copy of the hearth tax return for each shire was sent to the Exchequer: this is the return for Suffolk for Lady Day (25 March) 1674 (E 179/257/14) as printed in 1905 as Suffolk Green Book no xi, vol. 13. The numbers given are the numbers of hearths: where two or more people are grouped together with one number, it may be assumed that they were heads of separate households sharing a single building with that number of chimneys.GURDON. Cost: £6.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge
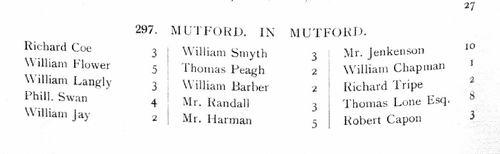
| Allegations for marriages in southern England
(1660-1679)
The province or archbishopric of Canterbury covered all England and Wales except for the northern counties in the four dioceses of the archbishopric of York (York, Durham, Chester and Carlisle). Marriage licences were generally issued by the local dioceses, but above them was the jurisdiction of the archbishop, exercised through his vicar-general. Where the prospective bride and groom were from different dioceses it would be expected that they obtain a licence from the archbishop; in practice, the archbishop residing at Lambeth, and the actual offices of the province being in London, which was itself split into myriad ecclesiastical jurisdictions, and spilled into adjoining dioceses, this facility was particularly resorted to by couples from London and the home counties, although there are quite a few entries referring to parties from further afield. The abstracts of the allegations given here usually state name, address (street in London, or parish), age, and condition of bride and groom; and sometimes the name, address and occupation of the friend or relative filing the allegation. Where parental consent was necessary, a mother's or father's name may be given. The ages shown should be treated with caution; ages above 21 tended to be reduced, doubtless for cosmetic reasons; ages under 21 tended to be increased, particularly to avoid requiring parental consent; a simple statement 'aged 21' may merely mean 'of full age' and indicate any age from 21 upwards. These are merely allegations to obtain licences; although nearly all will have resulted in the issuing of the licence, many licences did not then result in marriage. This index also includes marriage licence allegations for the jurisdiction of the Dean and Chapter of Westminster, 1558 to 1699.GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Allegations for marriages in southern England
(1687-1694)
The province or archbishopric of Canterbury covered all England and Wales except for the northern counties in the four dioceses of the archbishopric of York (York, Durham, Chester and Carlisle). Marriage licences were generally issued by the local dioceses, but above them was the jurisdiction of the archbishop, exercised through his vicar-general. Where the prospective bride and groom were from different dioceses it would be expected that they obtain a licence from the archbishop; in practice, the archbishop residing at Lambeth, and the actual offices of the province being in London, which was itself split into myriad ecclesiastical jurisdictions, and spilled into adjoining dioceses, this facility was particularly resorted to by couples from London and the home counties, although there are quite a few entries referring to parties from further afield. The abstracts of the allegations given here usually state name, address (street in London, or parish), age, and condition of bride and groom; and sometimes the name, address and occupation of the friend or relative filing the allegation. Where parental consent was necessary, a mother's or father's name may be given. The ages shown should be treated with caution; ages above 21 tended to be reduced, doubtless for cosmetic reasons; ages under 21 tended to be increased, particularly to avoid requiring parental consent; a simple statement 'aged 21' may merely mean 'of full age' and indicate any age from 21 upwards. These are merely allegations to obtain licences; although nearly all will have resulted in the issuing of the licence, many licences did not then result in marriage. GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

| Treasury Books
(1693-1696)
Records of the Treasury administration in Britain, America and the colonies, from January 1693 to March 1696. These also include records of the appointment and replacement of customs officers such as tide waiters and surveyors. The calendar was prepared by William A. Shaw for the Lords Commissioners of His Majesty's Treasury and published in 1935, from letters patent, privy seals, royal sign manuals and warrants, treasury warrants, commissions, orders, letters, memorials, reports and other entries, all not of the nature of Treasury Minutes. GURDON. Cost: £4.00.  | Sample scan, click to enlarge

|
Research your ancestry, family history, genealogy and one-name study by direct access to original records and archives indexed by surname.
|